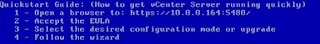
- Once you have completed your deployment of the appliance and powered it on, you can open the console view in the vSphere Client to get a quick glimpse at what is in store for configuration. You need to have DHCP enabled on the assigned network mapping to get the IP in step 1 to present.
- Note: If you are doing a greenfield deployment with 5.5 as I am, there is a feature to be aware. You will need to kill Tomcat before continuing or the Wizard will fail. Use the console or SSH to your new instance and type service vmware-vpxd stop at the prompt and hit enter. This will stop the vpxd service - not doing this will cause errors. I haven't found this formally documented anywhere unfortunately rather through trial and error.
- Navigating to the DHCP assigned IP - https://10.0.0.164:5480/ - you will get hit with the much expected certificate warning. Depending on your browser, methods for bypassing this vary. (Hopefully since you are deploying vCenter you know how to add a security exception for your browser!).
- Assuming use of a Static IP - close out of the Wizard.
- Click on the Network tab
- Select the Address Button
- Change the IPv4 Address Type to Static - you now can change the hostname. Fill in the desired hostname, IP, gateway, DNS Server, mask, and save the settings.
- The network changes made will require reloading the URL for management to your new static IP. Log back in and under utilities Launch the Setup Wizard.
- Follow along on the setup wizard:
- Log in with the default username/password combination of root/vmware and accept the EULA.
- Enable or leave disabled (my choice) data collection
- Select the custom configuration radio button. You will get to define each step except NTP here. NTP will use the specified Active Directory PDC Emulator provided time.
- Check the Active Directory Enabled box & Fill in the appropriate values for your domain
- For SSO select Embedded as well, just like the DB. Enter a password for the administrator account.
- With authentication configured for Active Directory the the time options automatically get configured to utilize AD synchronization.
- Once reviewed and configuration initiated all of the above options shoudl succeed.

- Click close and you should be up and running:
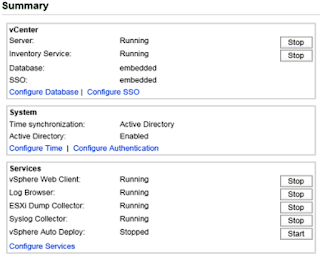
A couple of considerations:
Database Settings
Why did I choose to use the embedded DB? In this setup I don't have a separate SQL server for the database. Given I just have a small two node lab, this isn't an issue. Keep in mind, VMware only supports external Oracle databases. Fortunately the embedded PostgreSQL database will support up to 1,000 hosts and 10,000 virtual machines. If you are surpassing those numbers, you probably have access to Oracle. I am not so fortunate.
Sizing
By default the Services configurations are for small environments. I will leave my Services configurations at the default settings. This is one screen where the settings will impact multiple settings including modifications to the VM which runs the appliance. Reference KB2057376 to review large scale deployment tuning.
At this point you have a vCenter Server Appliance that is online with a static IP and communicating with Active Directory. Now go over to the Admin tab and change the root password. You can open up an Adobe Flash enabled web browser and navigate to <IP>:9443 to access to portal of your new vSphere Web Client. Right now only root can log in - something we will want to take care of down the road.
So now you have the vCenter appliance up and running! Great! Oh, yeah, we don't have any hosts or VMs to manage yet! I'll have to get to this next time.
No comments:
Post a Comment